Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakai, Satoshi*; Hirano, Shinichi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.491 - 496, 2021/12
After Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, various corrosion mitigating activities have been treated, and severe corrosion incident have never taken placed. On the other hand, the facilities were exposed sea water, and some of them have continuously exposed to ground water. The exposure of metal materials to environmental water has a risk of microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC). In this paper, we summarize the latest knowledge of MIC and the task of MIC in the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Ioka, Ikuo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Kawai, Daisuke*; Yokota, Hiroki*; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00377_1 - 19-00377_11, 2020/06
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen with high cost performance. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment. It was confirmed that the construction of the container with high corrosion resistance in sulfuric acid was possible in the hybrid technique.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2019/05
A thermochemical water-splitting iodine-sulfur processes (IS process) is one of candidates for the large-scale production of hydrogen using heat from solar power. Severe corrosive environment which is thermal decomposition of sulfuric acid exists in the IS process. A hybrid material with the corrosion-resistance and the ductility was made by a plasma spraying and laser treatment. The specimen had excellent corrosion resistance in the condition of 95 mass% boiling sulfuric acid. This was attributed to the formation of SiO on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment.
on the surface. To confirm the production characteristics of a container using the hybrid material, the container which has a welded part, a chamfer, a curved surface was experimentally made. There was no detachment in the plasma spraying and laser treated layer of the container after the laser treatment.
 -ray spectrometry; Application of
-ray spectrometry; Application of  pre-concentration from large volume of water sample using Powdex resin and barium sulfate coprecipitation of radium isotopes
pre-concentration from large volume of water sample using Powdex resin and barium sulfate coprecipitation of radium isotopesTomita, Jumpei; Abe, Takuya
JAEA-Research 2016-026, 12 Pages, 2017/03
An analytical method of low-level Ra isotopes in freshwater samples with combination of  pre-concentration from large volume of water sample (
pre-concentration from large volume of water sample ( 170 L) using Powdex resin and
170 L) using Powdex resin and  -ray spectrometry followed by simple coprecipitation of Ra was developed.
-ray spectrometry followed by simple coprecipitation of Ra was developed.  pre-concentration of Ra by batch method using Powder resin was examined, and it was shown that the amount of the resin required collecting Ra in the water sample could be determined by measuring the electric conductivity (EC) of water sample. It was found that coprecipitation of Ra with barium sulfate could remove more than 96% of potassium that increases the background. The validation of this method was confirmed by the analyses of 170 L of water sample containing the known amount of Ra isotopes with different EC. Among the analyses, the recovery of Ra was 98% in average and detection limits of
pre-concentration of Ra by batch method using Powder resin was examined, and it was shown that the amount of the resin required collecting Ra in the water sample could be determined by measuring the electric conductivity (EC) of water sample. It was found that coprecipitation of Ra with barium sulfate could remove more than 96% of potassium that increases the background. The validation of this method was confirmed by the analyses of 170 L of water sample containing the known amount of Ra isotopes with different EC. Among the analyses, the recovery of Ra was 98% in average and detection limits of  Ra and
Ra and 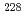 Ra were achieved to be approximately 0.3 and 0.5 mBq L
Ra were achieved to be approximately 0.3 and 0.5 mBq L , respectively.
, respectively.
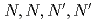 -tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide
-tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamideSasaki, Yuji; Suzuki, Tomoya; Morita, Keisuke; Yoshizuka, Kazuharu*
Hydrometallurgy, 159, p.107 - 109, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.3(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The novel tridentate extractant including soft donor has developed and examined. The extractant, tetraoctyl-thiodiglycolamide (S-DGA), is analogous structure to tetraoctyl-diglycolamide (TODGA), but with sulfur donor instead of ether oxygen of TODGA. S-DGA has unique property to extract silver from acidic solutions to n-dodecane with relatively high D values. We investigated the extraction behavior of Ag in various acids, HNO , H
, H SO
SO , and HClO
, and HClO .
.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Ota, Hiroyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Onuki, Kaoru; Hino, Ryutaro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 5(1), p.68 - 75, 2006/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting R&D on high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) technology and also on thermo-chemical water splitting hydrogen production technology by using an iodine-sulfur cycle (IS process) in the high temperature engineering test reactor (HTTR) project. The sulfuric acid (H SO
SO ) decomposer is one of the key equipments in the IS process, in which concentrated sulfuric acid is evaporated and decomposed into SO
) decomposer is one of the key equipments in the IS process, in which concentrated sulfuric acid is evaporated and decomposed into SO and H
and H O with the heat of high temperature helium gas supplied by HTGR. A concept of the decomposer consisting of multi-block-type heat exchanger made of SiC ceramics was proposed, and its feasibility was examined by preliminary analyses of thermal-hydraulic and structural strength and test-fabrication of SiC block components as well as elementary tests of seal performance in SiC blocks and metal flanges.
O with the heat of high temperature helium gas supplied by HTGR. A concept of the decomposer consisting of multi-block-type heat exchanger made of SiC ceramics was proposed, and its feasibility was examined by preliminary analyses of thermal-hydraulic and structural strength and test-fabrication of SiC block components as well as elementary tests of seal performance in SiC blocks and metal flanges.
Fukushi, Keisuke*; Sato, Tsutomu*; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Minato, Junichi*; Yamada, Hirohisa*
American Mineralogist, 89(11-12), p.1728 - 1734, 2004/11
The sorption mechanism of As(V) on schwertmannite was investigated by both a batch sorption experiment and crystallographic considerations. The batch experiment was carried out as a function of As(V) concentration in acidic solution at 25  C. Crystallographic considerations indicate surface sites of schwertmannite comprise varied surface oxygen (hydroxyl) and SO
C. Crystallographic considerations indicate surface sites of schwertmannite comprise varied surface oxygen (hydroxyl) and SO groups. Sorption experiments showed reactive surface sites for As(V) sorption are surface SO
groups. Sorption experiments showed reactive surface sites for As(V) sorption are surface SO groups. As(V) sorption mechanism involves ligand exchange with solid phase SO
groups. As(V) sorption mechanism involves ligand exchange with solid phase SO . Results also suggest monodentate As(V) coordination with surface adsorbed SO
. Results also suggest monodentate As(V) coordination with surface adsorbed SO sites and bidentate As(V) coordination in structural originated SO
sites and bidentate As(V) coordination in structural originated SO sites. Estimated equilibrium constant for ligand exchange reaction describes the observed As(V) sorption behavior. The surface structure approach in this study reveals reactive surface sites in As(V) sorption on schwertmannite comprise surface SO
sites. Estimated equilibrium constant for ligand exchange reaction describes the observed As(V) sorption behavior. The surface structure approach in this study reveals reactive surface sites in As(V) sorption on schwertmannite comprise surface SO group instead of surface hydroxyl groups identified by former views.
group instead of surface hydroxyl groups identified by former views.
Ishiyama, Shintaro; Maruyama, Shigeki*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, Supplement, Vol.112, No.1 (CD-ROM), p.S159 - S166, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Takaumi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Ozaki, Takuo; Arisaka, Makoto*; Yoshida, Zenko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.233 - 239, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Taniguchi, Naoki; Kawasaki, Manabu*; Fujiwara, Kazuo*
JNC TN8400 2001-011, 62 Pages, 2001/03
The corrosion of metallic materials used in natural environment are sometimes affected by microbial action. It is apprehended that microorganism living in deep underground or brought from ground surface during excavation makes an impact on overpack material for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. Sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) is known to be one of the most representative microorganism which affects the corrosion of metals. In this study, the behavior of growth of SRB was investigated at first under the presence of bentonite as a main component of buffer material which encloses the overpack. The results of the tests showed that the population of SRB after the culture in synthetic sea water mixed with bentonite decreased with increasing the ratio of bentonite/solution. SRB was hardly grown in medium whose bentonite/solution ratio exceeded 1000g/l. As a conservative case, the effects of sulfide on the corrosion of overpack materials were also studied assuming high activity of SRB. Carbon steel, copper and titanium specimens were immersed in synthetic sea water purging 0.1MPa H S gas and the corrosion behavior was compared with the results in N
S gas and the corrosion behavior was compared with the results in N gas purging environment. Obvious effect of sulfide on the corrosion of carbon steel was not observed, but the corrosion rates of copper specimens were accelerated several hundred times by purging H
gas purging environment. Obvious effect of sulfide on the corrosion of carbon steel was not observed, but the corrosion rates of copper specimens were accelerated several hundred times by purging H S gas. The absorption of hydrogen into titanium specimens was not affected by purging H
S gas. The absorption of hydrogen into titanium specimens was not affected by purging H S gas, but the difference of hydrogen absorption between pure titanium and titanium alloy containing 0.06%-Pd was observed.
S gas, but the difference of hydrogen absorption between pure titanium and titanium alloy containing 0.06%-Pd was observed.
Onuki, Kaoru; Akino, Norio; Shimizu, Saburo; Nakajima, Hayato; Higashi, Shunichi; Kubo, Shinji
JAERI-Tech 2001-032, 63 Pages, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
JNC TN8400 2000-030, 17 Pages, 2000/12
As a representative of natural marine groundwater, the author selected pumped water from a Quaternary sedimentary aquifer of the Mobara gas-field in Japan and measured the concentration of total organic carbon (TOC) and of organic acid anions (formic, acetic, lactic, succinic, humic, fulvic, propionic, valeric and butyric acids). The concentration of TOC ranged from 22 1 to 24
1 to 24 0mg/L. As organic acid anions, only succinic and fulvic acids were detected and each concentration was given to be from 5.8
0mg/L. As organic acid anions, only succinic and fulvic acids were detected and each concentration was given to be from 5.8 0.5 to 8.3
0.5 to 8.3 0.3 and from 3.3
0.3 and from 3.3 0.2 to 3.5
0.2 to 3.5 0.2mg/L, respectively. By consideration of the temperature and the [SO
0.2mg/L, respectively. By consideration of the temperature and the [SO
 ] of the groundwater, it is inferred that the organic acid has been significantly decomposed by activities of microbes, such as the fermentation process, CH
] of the groundwater, it is inferred that the organic acid has been significantly decomposed by activities of microbes, such as the fermentation process, CH COO
COO + H
+ H O = HCO
O = HCO
 + CH
+ CH .
.
Iwase, Masanori*
JNC TJ8400 2000-063, 78 Pages, 2000/03
This study is aimed at controlling oxidation reaction of molten metal by ash in incineration systems, and at positively utilizing the oxidation reaction for decontamination of slag. In this year, in order to investigate physico-chemical properties of mixed fused salt containing alkali sulfates, with special focus on the behaviour of oxygen anion in the melts, Cu / Cu
/ Cu redox equilibrium experiments were carried out. Among the effect of various parameters on Cu
redox equilibrium experiments were carried out. Among the effect of various parameters on Cu / Cu
/ Cu ratio in binary and ternary alkali sulfate melts, the effect of partial pressures of oxygen and SO
ratio in binary and ternary alkali sulfate melts, the effect of partial pressures of oxygen and SO was mainly investigated in the study. Variation in Cu
was mainly investigated in the study. Variation in Cu / Cu
/ Cu ratio were presented as the function of partial pressures of oxygen and SO
ratio were presented as the function of partial pressures of oxygen and SO , respectively. Possible thermodynamic interpretation were made on the experimental results. In addition, the dissolution of Cr
, respectively. Possible thermodynamic interpretation were made on the experimental results. In addition, the dissolution of Cr O
O in mixed alkali sulfates were also investigated as a first step to elucidate the mechanism of hot corrosion. With this investigation, an important finding was obtained that the solubility of Cr
in mixed alkali sulfates were also investigated as a first step to elucidate the mechanism of hot corrosion. With this investigation, an important finding was obtained that the solubility of Cr O
O for melts with same average ionic radius, in other words, oxygen ion activity, were essentially identical under constant temperature and atmosphere.
for melts with same average ionic radius, in other words, oxygen ion activity, were essentially identical under constant temperature and atmosphere.
Imai, Jun*
JNC TJ8400 2000-008, 196 Pages, 2000/02
The objective of this research is to make clear long-term alteration processes of bentonite contacting with concrete under a repository condition for radioactive waste. The Uzu tunnel in yamagata prefecture in Japan, constructed during the term of December of 1963 to July 1967, was selected as an appropriate natural analogue: the tunnel wall was made of portland cement and which has been contacting with a bentonite bed during 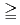 32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na
32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na -type and it changed to Ca
-type and it changed to Ca -type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca
-type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO
leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO  Al
Al O
O
 3CaSO
3CaSO 4
4  32H
32H O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.
O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yui, Mikazu; Randolph C Arthu*
JNC TN8400 99-074, 84 Pages, 1999/12
Hydrochemical investigation of Tertiary sedimentary rocks at JNC's Tono in-situ tests site indicate the groundwaters are: (1)meteoric in origin, (2)chemically reducing at depths greater than a few tens of meters in the sedimentary rock, (3)relatively old [carbon-14 ages of groundwaters collected from the lower part of the sedimentary sequence range from 13,000 to 15,000 years BP (before present)] (4)Ca-Na-HCO type solutions near the surface, changing to Na-HCO
type solutions near the surface, changing to Na-HCO type groundwaters with increasing depth. The chemical evolution of the groundwaters is modeled assuming local equilibrium for selected mineral-fluid reactions, taking into account the rainwater origin of these solutions. Results suggest it is possible to interpret approximately the "real" groundwater chemistry (i.e., pH, Eh, total dissolved concentrations of Si, Na, Ca, K, Al, carbonate and sulfate) if the following assumptions are adopted: (1)CO
type groundwaters with increasing depth. The chemical evolution of the groundwaters is modeled assuming local equilibrium for selected mineral-fluid reactions, taking into account the rainwater origin of these solutions. Results suggest it is possible to interpret approximately the "real" groundwater chemistry (i.e., pH, Eh, total dissolved concentrations of Si, Na, Ca, K, Al, carbonate and sulfate) if the following assumptions are adopted: (1)CO concentration in the gas phase contacting pore solutions in the overlying soil zone = 10
concentration in the gas phase contacting pore solutions in the overlying soil zone = 10 bar, (2)minerals in the rock zone that control the solubility of respective elements in the groundwater include; chalcedony (Si), albite (Na), kaolinite (Al), calcite (Ca and carbonate), muscovite (K) and pyrite (Eh and sulfate). It is noted, however, that the available field data may not be sufficient to adequately constrain parameters in the groundwater evolution model. In particular, more detailed information characterizing certain site properties (e.g., the actual mineralogy of "plagioclase", "clay" and "zeolite") are needed to improve the model. Alternative conceptual models of key reactions may also be necessary. For this reason, a model that accounts for ion-exchange reactions among clay minerals, and which is based on the results of laboratory experiments, has also been evaluated in the present study. Further improvements of model considering ion-exchange reactions are needed in future, however.
bar, (2)minerals in the rock zone that control the solubility of respective elements in the groundwater include; chalcedony (Si), albite (Na), kaolinite (Al), calcite (Ca and carbonate), muscovite (K) and pyrite (Eh and sulfate). It is noted, however, that the available field data may not be sufficient to adequately constrain parameters in the groundwater evolution model. In particular, more detailed information characterizing certain site properties (e.g., the actual mineralogy of "plagioclase", "clay" and "zeolite") are needed to improve the model. Alternative conceptual models of key reactions may also be necessary. For this reason, a model that accounts for ion-exchange reactions among clay minerals, and which is based on the results of laboratory experiments, has also been evaluated in the present study. Further improvements of model considering ion-exchange reactions are needed in future, however.
*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Ioka, Ikuo; Onuki, Kaoru; Shimizu, Saburo; Eto, Motokuni; Oku, Tatsuo*; *
Zairyo, 48(7), p.746 - 752, 1999/07
no abstracts in English
Ioka, Ikuo; Onuki, Kaoru; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kuriki, Yoshiro*; Nagoshi, Masayasu*; Nakajima, Hayato; Shimizu, Saburo
Ryusan To Kogyo, 52(4), p.1 - 6, 1999/04
no abstracts in English

 and AnO
and AnO
 Species in Geologic Environments
Species in Geologic EnvironmentsChoppin, G. R.*; Bronikowski, M.*; Chen, J.*; Byegard, J.*; Rai, D.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-012, 155 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of pentavalent and hexavalent actinide species (AnO and AnO
and AnO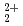 ) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO
) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. The estimation of the stability constants by use of the Born equation is included. The Pitzer parameters for AnO and AnO
and AnO
 , redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
, redox potentials and equilibrium constants of redox reactions for actinides are also included.
Rai, D.*; Rao, L.*; Weger, H. T.*; GREGORY R.CHOPPI*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-010, 95 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of Pu(III), Am(III), and Cm(III) in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system for high-level radioactive wastes. Thermodynamic data for the formation of complexes or compounds with hydroxide, chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate are discussed in this report. Where data for specific actinide(III) species are lacking, the data were selected based on chemical analogy to other trivalent actinides. In this study, the Pitzer ion-interaction model is mainly used to extrapolate thermodynamic constants to zero ionic strength at 25 C.
C.
Ioka, Ikuo; *; ; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Onuki, Kaoru
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 63(5), p.609 - 612, 1999/00
no abstracts in English